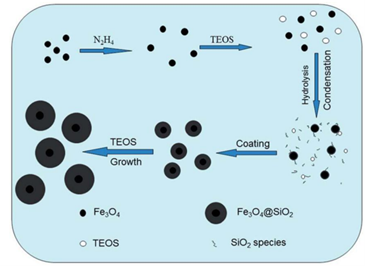
Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads
pH is very important in DNA Extraction and the reasons are as follows:
1. Maintaining DNA Stability
DNA remains relatively stable in solutions with a pH greater than 5 and less than 9. When the pH is excessively high (e.g., above 12) or low (e.g., below 3), the hydrogen bonds between the DNA double strands will dissociate, leading to DNA denaturation. For instance, Buffer II contains 0.2 M NaOH in plasmid DNA extraction, resulting in a system pH of 12. 6, which induces denaturation of both chromosomal and plasmid DNA. Consequently, it is necessary to adjust the pH back to neutrality in subsequent steps. This serves two purposes: first, it allows the denatured plasmid DNA to renature and remain stable; second, it leverages the difference in fragment size between genomic DNA and plasmid DNA (with plasmids being smaller and more likely to reanneal into dsDNA, while gDNA, being too long, cannot fully reanneal and instead becomes entangled, precipitating with SDS-protein complexes under the influence of high salt concentrations in buffer III).
2. Preventing DNA Degradation
EDTA can bind to metal ions such as Mg²⁺and Ca²⁺present in the solution. These metal ions are cofactors for DNase. EDTA inhibits the activity of DNase, thereby preventing the degradation of DNA by chelating these metal ions.
3. Optimizing Extraction Efficiency
Research has shown that the optimal pH for DNA extraction is 7.4. DNA extraction yield is maximized when buffer with pH 7. 4. The further the pH deviates from this value, the lower the DNA extraction yield. For example, the DNA extraction yield at pH 7.4 is 1.09, 1.03, 1.06, and 1.11 times that at pH 7.2, 7.6, 7.8, and 8.0, respectively.
Facilitating Nucleic Acid Binding to Magnetic Beads: An appropriate pH can promote the binding of nucleic acids to magnetic beads in magnetic bead-based DNA extraction methods. A high-salt binding buffer can neutralize the negative charges of nucleic acids, reducing the electrostatic repulsion between nucleic acids and magnetic beads, thereby facilitating the adsorption of nucleic acids onto the surface of the beads.
4. Protecting Lysozyme Activity
Lysozyme is utilized during the extraction of plasmid DNA from Gram-positive bacteria. Lysozyme is a glycoside hydrolase that can hydrolyze the β-1, 4 glycosidic bonds in peptidoglycan, the main chemical component of the cell wall of G+ bacteria, thereby exerting a lytic effect. The activity of lysozyme is inhibited when the pH of the buffer is less than 8. Therefore, it is essential to maintain an appropriate pH to ensure the activity of lysozyme.
5. Improving Elution Efficiency
The pH of the elution buffer significantly affects the efficiency of DNA elution. The pH of the elution buffer should be maintained between 7.0 and 8.5 to ensure that DNA is fully eluted. A pH that is too low will reduce the elution efficiency.
In summary, the adjustment of pH is crucial in the DNA extraction process. It not only helps to maintain the stability of DNA and prevent degradation but also optimizes extraction efficiency, protects the activity of relevant enzymes, and optimizes elution conditions.
Supplier
Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 which is a professional manufacturer of biomagnetic materials and nucleic acid extraction reagents.
We have rich experience in nucleic acid extraction and purification, protein purification, cell separation, chemiluminescence, and other technical fields.
Our products are widely used in many fields, such as medical testing, genetic testing, university research, genetic breeding, and so on. We not only provide products but also can undertake OEM, ODM, and other needs. If you have a related need, please feel free to contact us at sales01@lingjunbio.com.