Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads
In the field of genomics, the study of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is gradually becoming a hot topic. Free DNA refers to small fragments of DNA present in the blood, which are mainly released into the blood from apoptotic or damaged cells. cfDNA has become one of the important biomarkers for non-invasive diagnosis because it carries individual genetic information, including tumor DNA; this article will help you understand the latest progress in cell-free DNA extraction technology and its potential application in the field of medical health.
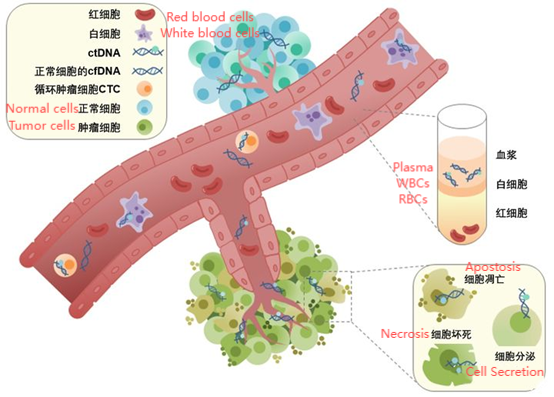
The discovery and importance of cell-free DNA
The history of free DNA (cell-free DNA, cfDNA) can be traced back to 1948 when scientists first reported the discovery of free DNA fragments in the blood. The earliest records show that free DNA was discovered in the blood by two French scientists, Mandel and Metais, in the 1940s. However, this discovery only attracted widespread attention after some time. It was only in the advancement of molecular biology technology and the deepening of its potential clinical application that the importance of free DNA gradually emerged.
With the development of high-throughput sequencing technology (Next Generation Sequencing, NGS), the application scope of cfDNA has been continuously expanded, not only limited to prenatal diagnosis, but also including early detection of cancer, post-transplantation monitoring and other fields. Today, free DNA has become a core component of liquid biopsy and an important tool in biomedical research.
Development of extraction technology
Free DNA is usually present in plasma or serum, with extremely low content, which brings challenges to extraction. Traditional extraction methods include phenol-chloroform extraction and commercial kits. Although the former can obtain higher DNA purity, it is not suitable for large-scale sample processing due to its complex operation and long consumption; the latter has been widely used in clinical practice due to its simple and fast characteristics.
In recent years, with the development of nanotechnology and microfluidics technology, new cfDNA extraction platforms have emerged. These platforms not only improve the recovery rate and purity of cfDNA, but also greatly shorten the processing time, making high-throughput analysis possible. In addition, magnetic bead separation technology can also effectively enrich cfDNA, providing a reliable guarantee for subsequent sequencing analysis.
Prospects for cell-free DNA extraction
Although cell-free DNA extraction technology has made significant progress, there are still some challenges to overcome, such as how to improve further the detection sensitivity of cfDNA and how to standardize the sample processing process. With the deepening of research and the advancement of technology, these problems will be solved. In the future, cell-free DNA extraction technology will play a more important role in personalized medicine, precision medicine, etc., and make greater contributions to human health.
Supplier Introduction

Shanghai Lingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2016 which is a professional manufacturer of biomagnetic materials and nucleic acid extraction reagents.
We have rich experience in nucleic acid isolation and purification, protein purification, cell separation, chemiluminescence and other technical fields.
Our products are widely used in many fields, such as medical testing, genetic testing, university research, genetic breeding, etc. We not only provide products but also can undertake OEM, ODM, and other needs. If you have related needs, please feel free to contact us at sales01@lingjunbio.com.