Professional Manufacturer of Biomagnetic Beads
The principle of the magnetic bead method for the extraction of small fragments of DNA is mainly based on the affinity between the biomagnetic beads and specific molecules modified on their surface and DNA, as well as on the changes in the conformation of the DNA molecule under different conditions. The following is a detailed explanation of the principle:
First,Characteristics and selection of biomagnetic beads:
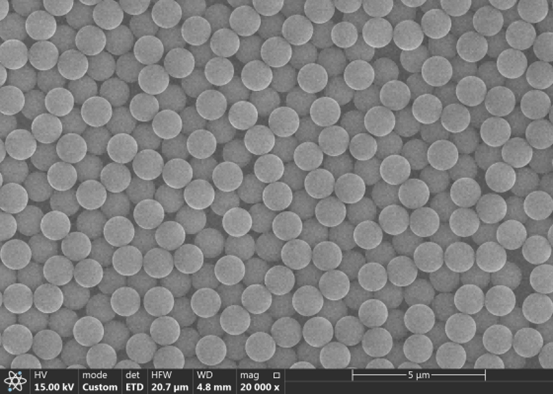
1. Characteristics: The biomagnetic beads used in the magnetic bead method are usually made of magnetic materials ( Fe3O4 or magnetite, etc.), which enable the beads to be separated and collected by magnetic force. The diameter of the magnetic beads is usually on the order of micrometers in order to form a good suspension in the solution.
2. Selection: When extracting small fragments of DNA, magnetic beads with specific molecules modified on their surface need to be selected. These modified molecules (oligonucleotides, nucleic acid binding proteins, etc.) are able to specifically bind to DNA, thus realizing the enrichment and separation of DNA.

Second, the binding mechanism of DNA and magnetic beads:
1. Affinity binding: Under appropriate conditions (such as specific pH, salt concentration and temperature), DNA molecules will be electrostatically bound to positively charged molecules (such as positively charged chemical groups) modified on the surface of the magnetic beads through the negative charge on its phosphate backbone. This binding is specific and ensures that only the target DNA molecule binds to the magnetic beads.
2. Molecular conformation change: In some cases, such as when PEG and salt ions are added, the conformation of the DNA molecule changes dramatically. From a linear shape is compressed to form a curly spherical shape, and this change makes the DNA easier to bind to the magnetic beads. At the same time, DNA molecules of different lengths will undergo selective precipitation under the action of PEG and salt ions, so that the separation of DNA fragments of different sizes can be realized.
Third, Extraction process of small fragment DNA:
1. Sample processing: First process the biological samples to release the DNA. this may include cell lysis, protein removal and other steps.
2. Magnetic bead binding: The treated sample is mixed with magnetic beads to bind DNA to the beads under suitable conditions. In this step, the binding efficiency of DNA to magnetic beads can be optimized by controlling the concentration of PEG and salt ions.
3. Washing and separation: Unbinding impurities and DNA fragments are removed using washing buffer. The beads are held magnetically to the side wall of the reaction vessel and the supernatant is then removed. This step can be repeated several times to ensure clean removal.
4. DNA elution: Under appropriate conditions (e.g. changing pH or ion concentration), the DNA is eluted from the magnetic beads. The DNA solution obtained at this time is the purified small DNA fragment .
Forth,the advantages of extracting small DNA fragments by magnetic bead method:
1. High efficiency: The magnetic bead method can extract DNA quickly and efficiently, especially suitable for high-throughput sample processing.
2. Simplicity: Magnetic bead method is easy to operate, without complex equipment and technology.
3. High purity: The magnetic bead method can effectively remove proteins, lipids and other impurities in the sample, thus obtaining high purity DNA.
4. Flexibility: The magnetic bead method can be applied to the extraction of DNA fragments of different sizes, and can optimize the extraction effect by adjusting the experimental conditions.
In summary, the principle of magnetic bead method to extract small fragments of DNA is mainly based on the affinity between magnetic beads and DNA as well as changes in the conformation of DNA molecules. By optimizing the experimental conditions and controlling the modifying molecules of the magnetic beads, efficient, easy and high-purity extraction of small DNA fragment can be achieved.
Related topics:
- The future of magnetic bead raw materials in the current trade barrier war between China and the United States
- 2025 IVD raw material market research report
- How long can whole blood samples be frozen?
- New era of biotechnology: AI and policy drive, innovative drug research and development to welcome the golden age
- Market research report of chemiluminescent magnetic beads(2025)